Industrial Robot Arms in Logistics: Order Fulfillment Applications
⚡Quick Facts
Technology Performance Metrics
⭐Key Features
✨Benefits
🎯Applications
📝Detailed Information
Technology Overview
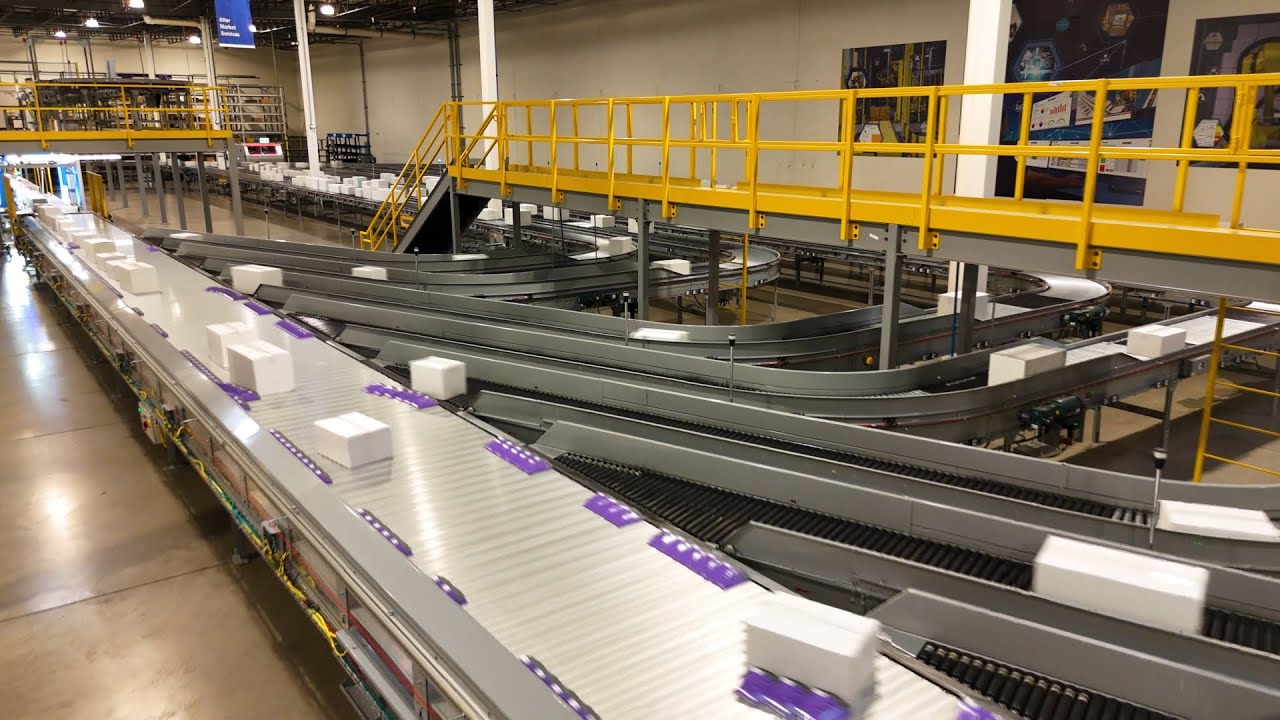
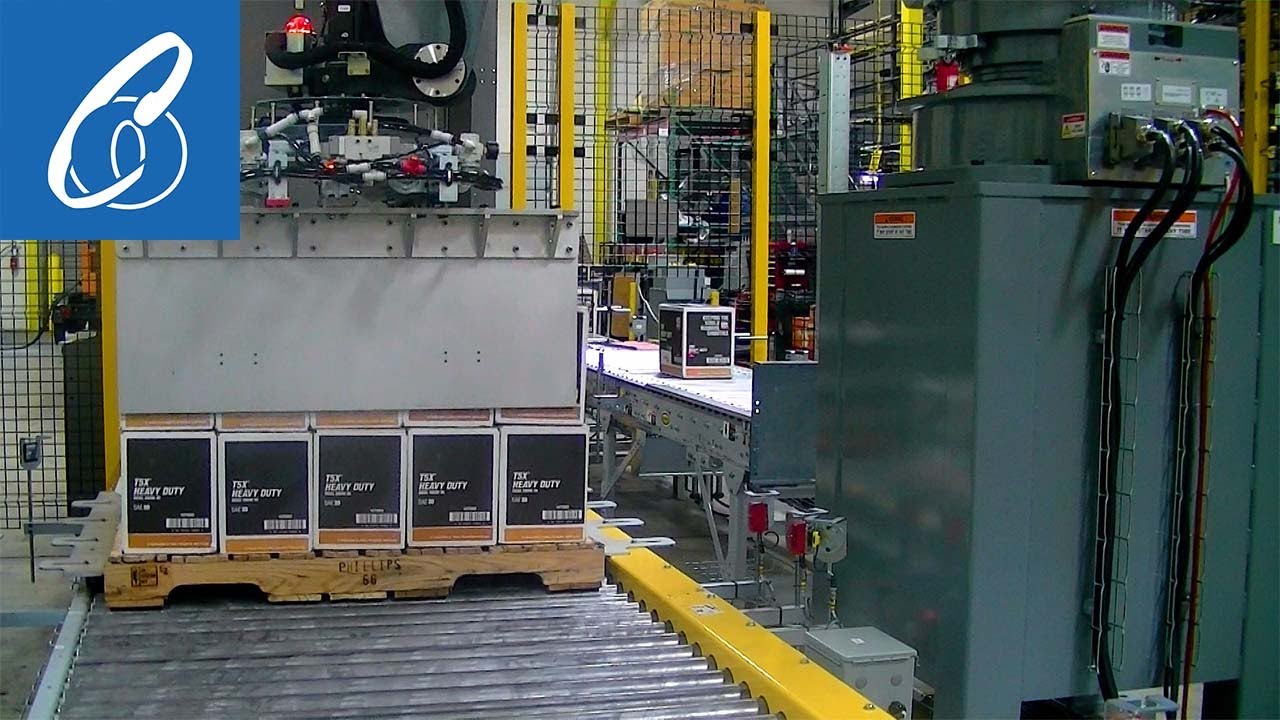
Industrial robot arms have become a versatile and powerful tool for automating a wide range of physical tasks within modern logistics and order fulfillment operations. Unlike fixed automation designed for a single purpose, these programmable, multi-axis arms can be equipped with various end-effectors (grippers, suction cups, etc.) and guided by vision systems to perform diverse functions. This flexibility makes them ideal for the logistics sector, which encompasses multiple, often repetitive, material handling processes that require precision, speed, and consistency. From the moment goods arrive on a pallet to the moment they leave as a completed order, robotic arms are being deployed to reduce manual labor, increase throughput, and improve workplace safety in distribution centers and third-party logistics (3PL) facilities.
How It Works
Core Principles
The core principle is using a programmable, multi-jointed robotic manipulator to perform specific material handling tasks. The robot's movements and logic are controlled by software, often integrated with sensors (like 2D/3D cameras) to locate and identify objects. Different end-of-arm tooling (EOAT) is used depending on the task—for example, a vacuum gripper for boxes, a mechanical gripper for bags, or a specialized tool for layer handling.
Key Features & Capabilities
The primary feature is the ability to automate multiple discrete tasks within the broader order fulfillment operation. Instead of a single-purpose machine, one technology platform (the industrial robot arm) can be adapted through programming and tooling. The video highlights specific application examples including mixed-case depalletizing (unloading varied boxes from a pallet), piece picking from totes and tubs (selecting individual items), order fulfillment (assembling items), case packing (loading items into shipping boxes), and mixed-case palletizing (building stable pallets of assorted cases).
Advantages & Benefits
The use of robotic arms enables automation across various stages of the logistics workflow, creating opportunities for efficiency gains at multiple touchpoints rather than just one. This widespread application improves overall operational efficiency and consistency in warehouse distribution centers and 3PL facilities, leading to higher throughput, reduced labor costs in repetitive tasks, and fewer product damages caused by manual handling.
Implementation Considerations
Considerations include the need for precise integration with upstream and downstream material flow (conveyors, etc.). The choice of end-effector and vision system is critical and depends heavily on the specific product characteristics (size, weight, packaging material). Successful implementation requires programming expertise and often a period of system tuning to reach optimal performance and reliability.
Use Cases & Applications
Ideal For
Industrial robot arms are ideal for medium to high-volume logistics operations where specific tasks are repetitive, physically demanding, or require high precision, and where the product mix, while diverse, is manageable within the robot's designed capabilities.
Conclusion
Industrial robot arms represent a foundational and highly adaptable automation technology for the logistics industry. Their ability to perform a spectrum of tasks—from depalletizing to palletizing—makes them a valuable asset for building more automated, efficient, and resilient fulfillment operations. While implementation requires careful planning and integration, the potential to automate key bottlenecks in the logistics workflow offers a compelling return on investment through labor savings, increased throughput, and improved operational consistency. As robotic technology continues to advance in perception and dexterity, its role in logistics is set to expand even further.